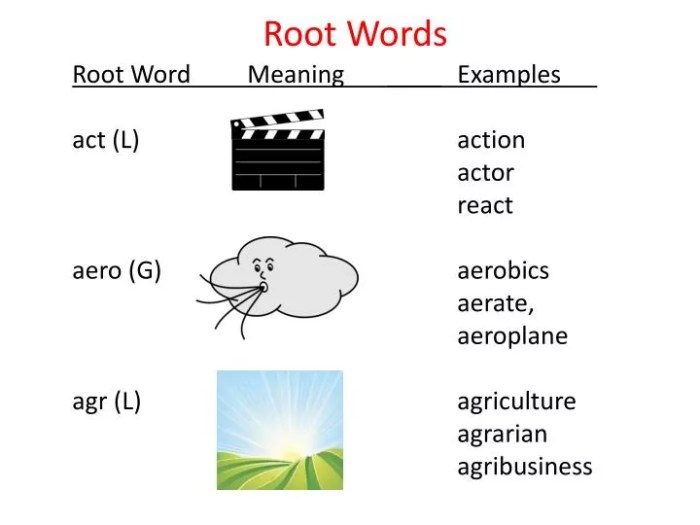
Words with the root word agri – Embark on a journey into the captivating realm of words with the root word ‘agri,’ where we unravel the intricate connections between language and the world of agriculture. From its humble origins to its profound impact on our lives, ‘agri’ weaves a tapestry of terms that illuminate the very essence of farming and its profound significance.
Delving into the etymology of ‘agri,’ we discover its Latin roots, where it signifies ‘field’ or ‘farm.’ This linguistic heritage forms the bedrock of a vast vocabulary that encompasses everything from agriculture and agronomy to agribusiness and agroforestry. As we delve deeper into this lexical landscape, we uncover a treasure trove of words that paint a vivid picture of the agricultural world.
Agriculture
Agriculture is the practice of cultivating crops and raising livestock. It has been a vital part of human civilization for thousands of years, providing sustenance and economic stability to societies worldwide.
History and Evolution of Agriculture
The origins of agriculture can be traced back to the Neolithic Revolution, which occurred around 10,000 BCE. During this period, humans transitioned from hunting and gathering to settled farming practices. The domestication of plants and animals allowed for a more reliable food supply, leading to population growth and the development of complex societies.
Over the centuries, agriculture has undergone significant advancements. The invention of the plow and irrigation systems increased crop yields, while the development of selective breeding techniques improved the quality of livestock.
In the 19th and 20th centuries, the Industrial Revolution brought about further advancements in agriculture, including the mechanization of farming practices and the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
Types of Agriculture
There are numerous types of agriculture, each with its own unique methods and products. Some of the most common types include:
- Subsistence agriculture:practiced by small-scale farmers who primarily grow crops for their own consumption.
- Commercial agriculture:involves large-scale farming operations that produce crops for sale in domestic or international markets.
- Pastoral agriculture:focuses on the raising of livestock, such as cattle, sheep, or goats.
- Organic agriculture:emphasizes the use of natural methods and materials in crop and livestock production, avoiding synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
Major Agricultural Products and their Global Significance
Agriculture produces a wide range of products that are essential for human sustenance and economic development. Some of the most important agricultural products include:
- Cereals:such as wheat, rice, and corn, are staple foods for billions of people worldwide.
- Fruits and vegetables:provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber for a healthy diet.
- Meat and dairy products:are major sources of protein and other nutrients.
- Fiber crops:such as cotton and flax, are used in the production of textiles and other materials.
- Biofuels:such as ethanol and biodiesel, are derived from agricultural products and offer renewable energy sources.
Agricultural Technology

The rapid advancement of agricultural technology is transforming farming practices worldwide. This technology enables farmers to optimize their operations, increase efficiency, and produce more food with fewer resources.
Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture involves using sensors, data analytics, and GPS technology to collect and analyze real-time data on crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns. This information allows farmers to make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, resulting in increased yields and reduced environmental impact.
Automation
Automation is playing a significant role in agriculture, from driverless tractors to robotic harvesting systems. These technologies free up farmers from labor-intensive tasks, allowing them to focus on strategic planning and management. Automation also improves efficiency and reduces the risk of human error.
In the realm of agriculture, the root word “agri” has given rise to numerous terms. One such term is “agronomy,” the study of soil management and crop production. Interestingly, the concept of “sphinx” also finds its roots in ancient Egypt, where the mythical creature with a human head and a lion’s body stood as a guardian of sacred knowledge.
The Alpha Phi Alpha Sphinx Head , a symbol of wisdom and leadership, echoes this ancient connection between agriculture and the enigmatic realm of the sphinx.
Data Analytics
Data analytics is essential for optimizing agricultural operations. Farmers can use data from sensors, weather stations, and historical records to identify patterns, predict crop yields, and make data-driven decisions. This information helps them plan for future seasons and adapt to changing conditions.
Innovative Agricultural Technologies
- Vertical farming:Growing crops in vertically stacked layers, maximizing space and reducing water consumption.
- Hydroponics:Growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions without soil, increasing yields and reducing disease.
- Gene editing:Modifying plant genes to enhance traits such as drought resistance, pest resistance, and nutritional value.
These advancements in agricultural technology are revolutionizing farming and helping to ensure a sustainable and productive food system for the future.
Agricultural Sustainability

Agricultural sustainability is a practice that seeks to meet the demands of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It encompasses the environmental, economic, and social dimensions of agriculture, aiming to ensure the long-term viability of agricultural systems.
Sustainable agriculture plays a crucial role in ensuring food security, mitigating climate change, and preserving biodiversity. It involves adopting practices that minimize environmental degradation, enhance soil health, and promote biodiversity.
Challenges in Sustainable Agriculture
- Climate change:Extreme weather events, rising temperatures, and changes in precipitation patterns pose significant challenges to agricultural production.
- Soil degradation:Soil erosion, nutrient depletion, and contamination can reduce soil fertility and productivity.
- Water scarcity:Agriculture is a major consumer of water, and increasing water scarcity can limit crop production.
- Pesticide and fertilizer use:Excessive use of pesticides and fertilizers can pollute water sources and harm wildlife.
Opportunities in Sustainable Agriculture
- Conservation tillage:Minimizing soil disturbance can reduce erosion, improve soil health, and conserve moisture.
- Crop rotation:Growing different crops in sequence can improve soil fertility, reduce disease, and enhance biodiversity.
- Integrated pest management:Combining biological, cultural, and chemical methods to control pests can minimize the need for synthetic pesticides.
- Precision agriculture:Using technology to optimize crop production and reduce environmental impacts.
Environmental Benefits of Sustainable Agriculture
- Reduced soil erosion:Sustainable practices such as conservation tillage help prevent soil loss and maintain soil health.
- Improved water quality:Reduced fertilizer and pesticide use can minimize water pollution and protect aquatic ecosystems.
- Increased biodiversity:Sustainable agriculture supports a diverse range of plant and animal species, enhancing ecosystem resilience.
- Carbon sequestration:Soil management practices can increase soil organic matter, which helps sequester carbon from the atmosphere.
Agricultural Economics: Words With The Root Word Agri

Agricultural economics applies economic principles to analyze the production, distribution, and consumption of agricultural products. It examines factors that influence farm-level decision-making, market behavior, and the overall performance of the agricultural sector.
Economic Principles and Factors
- Production costs:Land, labor, machinery, fertilizers, and other inputs affect the cost of producing agricultural goods.
- Supply and demand:The interaction between the quantity of agricultural products available and the demand for them determines prices.
- Market structure:The number and size of buyers and sellers in agricultural markets influence competition and pricing.
li> Government policies:Farm subsidies, trade tariffs, and environmental regulations impact agricultural production and markets.
Role of Government Policies and International Trade
Government policies can significantly influence agricultural economics by:
- Providing financial support to farmers
- Regulating agricultural production and marketing
- Promoting international trade
International trade plays a crucial role in agricultural economics by:
- Expanding markets for agricultural products
- Influencing prices and competition
- Promoting economic growth in both exporting and importing countries
Agricultural Economic Models, Words with the root word agri
Agricultural economic models are mathematical representations of the agricultural sector used to:
- Predict market outcomes
- Evaluate the impact of policies
- Optimize resource allocation
Examples of agricultural economic models include:
- Linear programming models
- Econometric models
- Simulation models
Agricultural Research and Development

Agricultural research and development (R&D) play a pivotal role in enhancing agricultural productivity, ensuring food security, and promoting sustainable farming practices. It involves the systematic study and experimentation to improve agricultural technologies, crop varieties, and farming methods.
Agricultural R&D encompasses a wide range of activities, including:
Crop Improvement
- Developing new crop varieties with improved yield, disease resistance, and nutritional value.
- Using genetic engineering techniques to enhance crop traits.
Livestock Production
- Improving animal breeding and genetics to increase productivity.
- Developing new vaccines and treatments for animal diseases.
Soil Management
- Studying soil fertility and nutrient management.
- Developing techniques to prevent soil erosion and degradation.
Water Management
- Optimizing irrigation systems to conserve water.
- Developing drought-tolerant crops and farming practices.
Major Agricultural Research Institutions
Numerous research institutions worldwide contribute significantly to agricultural R&D, including:
- International Rice Research Institute (IRRI)
- International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT)
- National Agricultural Research System (NARS)
These institutions have made substantial contributions to agricultural advancements, leading to increased crop yields, improved food quality, and more sustainable farming practices.
FAQ
What is the origin of the word ‘agriculture’?
The word ‘agriculture’ originates from the Latin words ‘ager’ (field) and ‘cultura’ (cultivation), reflecting its deep-rooted connection to the cultivation of land for food production.
What are some examples of words with the root word ‘agri’?
Examples of words with the root word ‘agri’ include agriculture, agronomy, agribusiness, agroforestry, agrarian, and agriculturalist.
How does ‘agricultural technology’ contribute to modern farming practices?
‘Agricultural technology’ encompasses a wide range of innovations that enhance farming practices, including precision agriculture, automation, data analytics, and biotechnology. These technologies optimize crop yields, reduce environmental impact, and improve the efficiency of agricultural operations.
What is the significance of ‘agricultural sustainability’?
‘Agricultural sustainability’ refers to farming practices that maintain the long-term health of ecosystems while meeting the needs of present and future generations. It involves balancing environmental, economic, and social considerations to ensure the viability of agriculture over time.
How does ‘agricultural economics’ influence the agricultural industry?
‘Agricultural economics’ analyzes the economic principles and factors that affect agricultural production, markets, and policies. It helps farmers make informed decisions, governments design effective agricultural policies, and consumers understand the economic implications of food production and consumption.