Delving into the intricacies of RNA and protein synthesis, the RNA and Protein Synthesis Gizmo Answer Key PDF serves as an invaluable resource, providing a comprehensive understanding of the fundamental processes that govern cellular life. Through its detailed explanations and guided exercises, this guide unlocks the secrets of gene expression, empowering readers to unravel the complexities of molecular biology.
As we embark on this scientific journey, we will explore the essential roles of RNA and proteins in cellular processes, deciphering the mechanisms of transcription and translation, and examining the profound impact of mutations on protein function. The RNA and Protein Synthesis Gizmo Answer Key PDF will illuminate these concepts with clarity and precision, fostering a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of the cellular world.
Introduction to RNA and Protein Synthesis
RNA (ribonucleic acid) and proteins are essential molecules involved in a wide range of cellular processes. RNA serves as the intermediary between DNA and proteins, carrying genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized.
Proteins, on the other hand, play crucial roles in virtually all cellular functions, including metabolism, cell signaling, and structural support. They are composed of amino acids linked together in a specific sequence determined by the genetic code.
Types of RNA
- Messenger RNA (mRNA): Carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA): Brings specific amino acids to the ribosomes during protein synthesis.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): Forms the core of ribosomes, where protein synthesis takes place.
Transcription
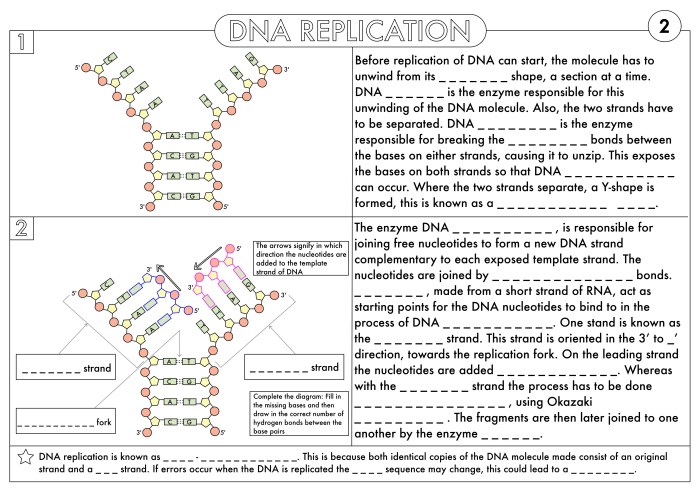
Transcription is the process by which the genetic information in DNA is copied into RNA. It occurs in the nucleus and involves the following key components:
- DNA template strand: The DNA strand that serves as the template for RNA synthesis.
- RNA polymerase: An enzyme that synthesizes RNA by adding nucleotides to the growing RNA chain.
- Promoter region: A specific DNA sequence that signals the start of transcription.
During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region and unwinds the DNA helix. It then synthesizes a complementary RNA strand, using the DNA template strand as a guide. The newly synthesized RNA strand is called a primary transcript, which undergoes further processing to form mature RNA molecules.
Translation
Translation is the process by which the genetic information in mRNA is converted into a protein. It occurs in the cytoplasm and involves the following key components:
- Ribosomes: Cellular structures that serve as the site of protein synthesis.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA): Molecules that bring specific amino acids to the ribosomes.
- Start codon: A specific mRNA sequence that signals the start of protein synthesis.
During translation, ribosomes bind to the mRNA and move along the strand, reading the genetic code in groups of three nucleotides called codons. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid, which is brought to the ribosome by the appropriate tRNA molecule.
The amino acids are then linked together to form a polypeptide chain, which folds into a specific three-dimensional structure to become a functional protein.
Mutations and Protein Synthesis
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can affect protein synthesis. They can be caused by a variety of factors, including errors during DNA replication, exposure to environmental toxins, and radiation.
Types of Mutations, Rna and protein synthesis gizmo answer key pdf
- Point mutations: Single-nucleotide changes in the DNA sequence.
- Insertion mutations: The addition of one or more nucleotides to the DNA sequence.
- Deletion mutations: The removal of one or more nucleotides from the DNA sequence.
Mutations can have a range of effects on protein synthesis. They can lead to the production of non-functional proteins, truncated proteins, or proteins with altered functions.
Gizmo Answer Key: Rna And Protein Synthesis Gizmo Answer Key Pdf
The following table provides answers to questions from the Gizmo activity on RNA and protein synthesis:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription? | RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA by adding nucleotides to the growing RNA chain. |
| What is the difference between mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA? | mRNA carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes, tRNA brings specific amino acids to ribosomes, and rRNA forms the core of ribosomes. |
| How does a mutation affect protein synthesis? | Mutations can lead to the production of non-functional proteins, truncated proteins, or proteins with altered functions. |
FAQ Section
What is the role of RNA in protein synthesis?
RNA serves as the intermediary molecule between DNA and protein, carrying genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosomes, where protein synthesis takes place.
How does transcription differ from translation?
Transcription involves the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template, while translation involves the synthesis of proteins from an RNA template.
What are the consequences of mutations on protein function?
Mutations can alter the amino acid sequence of proteins, potentially disrupting their structure and function, leading to various genetic disorders and diseases.