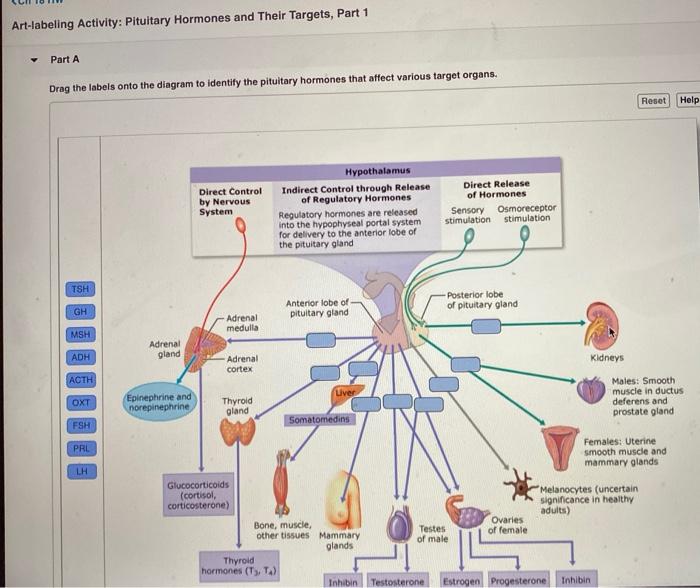
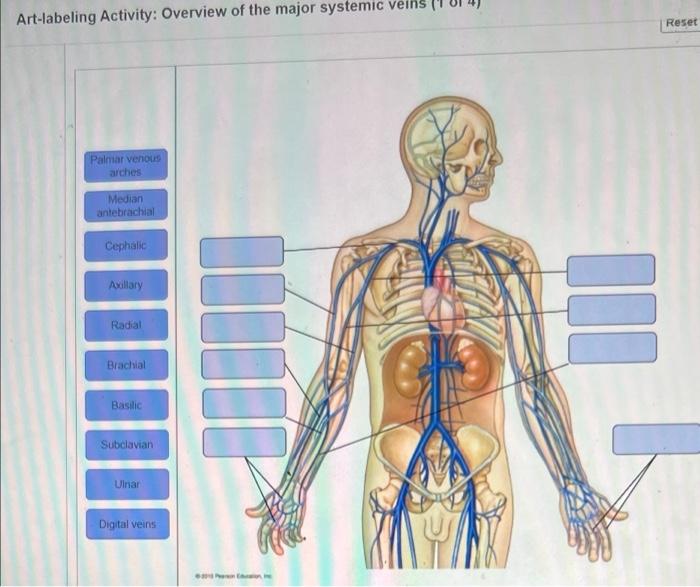
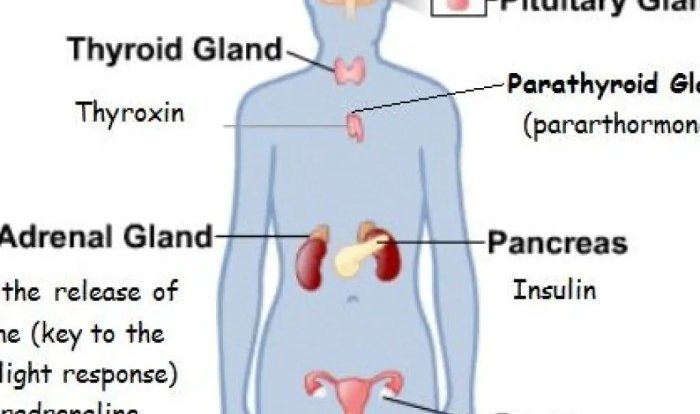
Embark on an educational journey with our art-labeling activity: overview of the endocrine organs. This interactive exploration provides a comprehensive understanding of these vital structures, their functions, and their impact on overall health.
Delve into the fascinating world of endocrinology, unraveling the intricate workings of the endocrine system and its pivotal role in regulating bodily processes.
Overview of the Endocrine Organs: Art-labeling Activity: Overview Of The Endocrine Organs
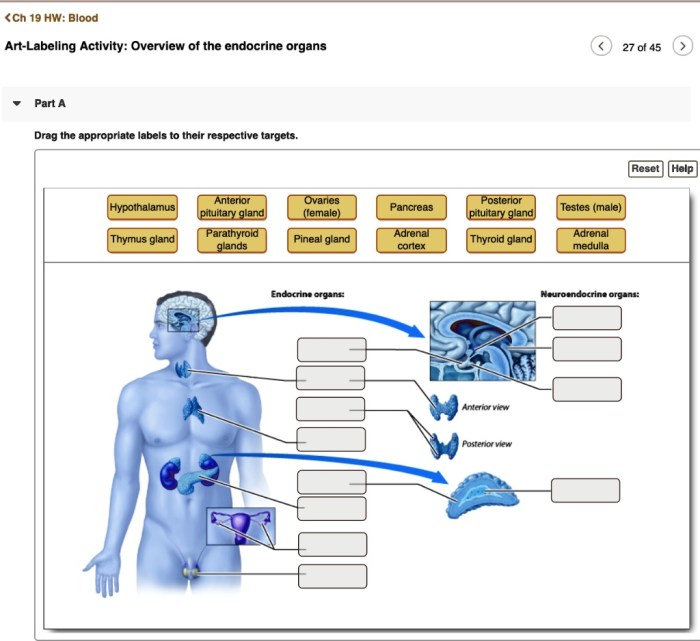
Endocrine organs are specialized glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones travel throughout the body and regulate various physiological processes, including metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood.
The discovery of endocrine organs dates back to the 19th century, with the identification of the pituitary gland as a key regulator of growth. Since then, research has uncovered the existence and functions of numerous other endocrine organs, providing a deeper understanding of their role in maintaining homeostasis.
Location and Structure
Major endocrine organs are located in various parts of the body, including the brain, neck, chest, and abdomen. They vary in size and shape, but all share the common feature of secreting hormones into the bloodstream.
Functions of the Endocrine Organs
The primary function of endocrine organs is to secrete hormones, which act as chemical messengers that regulate specific target tissues and organs.
Endocrine regulation is a complex process involving feedback mechanisms that ensure hormone levels are maintained within a narrow range. When hormone levels rise, negative feedback mechanisms are triggered to reduce secretion, while low hormone levels trigger positive feedback mechanisms to increase secretion.
Examples of specific hormones include insulin (secreted by the pancreas) which regulates blood sugar levels, and thyroxine (secreted by the thyroid gland) which regulates metabolism.
Types of Endocrine Glands, Art-labeling activity: overview of the endocrine organs
| Gland Name | Location | Hormones Produced | Functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pituitary Gland | Base of the brain | Growth hormone, prolactin, thyroid-stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone | Regulates growth, metabolism, reproduction, and stress response |
| Thyroid Gland | Neck | Thyroxine, triiodothyronine | Regulates metabolism |
| Adrenal Glands | Above the kidneys | Cortisol, adrenaline, aldosterone | Regulates stress response, blood pressure, and electrolyte balance |
| Pancreas | Abdomen | Insulin, glucagon | Regulates blood sugar levels |
Methods for Studying the Endocrine System
Various techniques are used to study the endocrine system, including:
- Blood tests to measure hormone levels
- Imaging techniques such as MRI and CT scans to visualize endocrine organs
- Genetic analysis to identify mutations that may cause endocrine disorders
These methods are essential for diagnosing and treating endocrine disorders.
Disorders of the Endocrine System
Common endocrine disorders include:
- Diabetes (impaired insulin production or function)
- Thyroid disorders (over- or underproduction of thyroid hormones)
- Adrenal insufficiency (decreased production of adrenal hormones)
These disorders can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being, and require appropriate treatment.
FAQs
What is the primary function of endocrine organs?
Endocrine organs secrete hormones, chemical messengers that regulate various bodily processes, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
How does the art-labeling activity enhance learning?
By actively labeling and identifying the endocrine organs, students reinforce their knowledge and develop a visual representation of the endocrine system.
What are some common endocrine disorders?
Diabetes, thyroid disorders, and adrenal insufficiency are examples of endocrine disorders that can disrupt hormonal balance and lead to various health issues.